Question 4
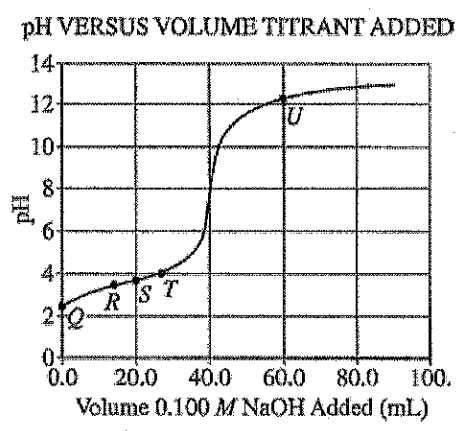
Equivalence occurs at 40.0 ml titrant added. So half equivalence at 20.0 ml of titrant.
At half equivalence, [HA]=[A-]. Below half equivalence, more acid species present.
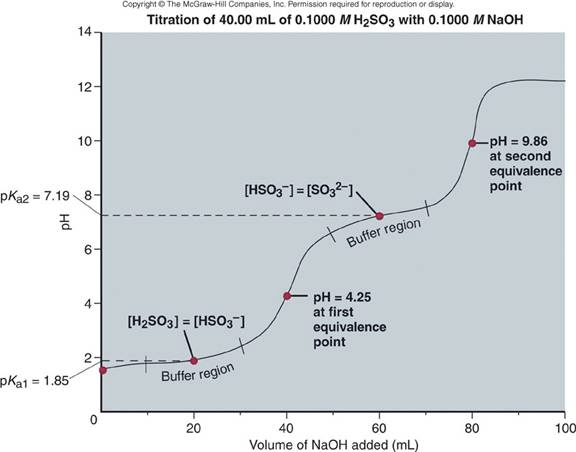
Question 8
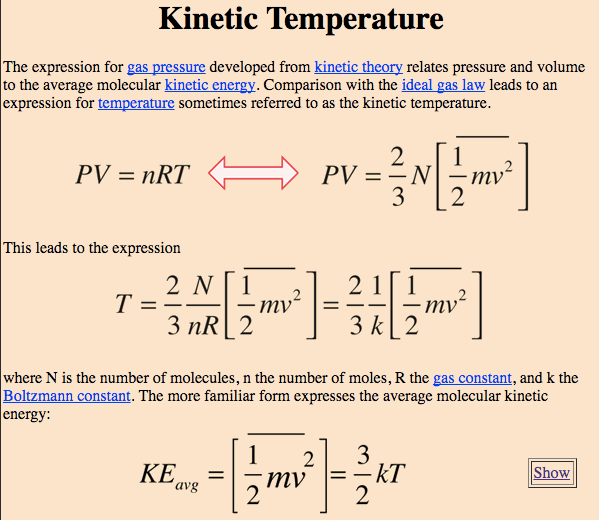
Question 19

Question 26
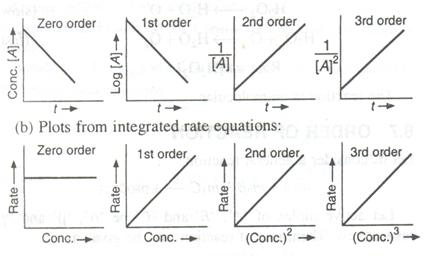
Question 25
- Larger ionic radius --> smaller lattice energy --> lower boiling point