Question 1 (a)
Write the state of each substance for dissolving equation
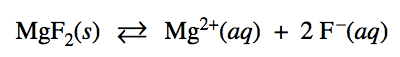
![The Solubility Expression AaBb(s) aAb+ (aq) + bBa- (aq) Ksp = [Ab+]a [Ba-]b Example:Pb12 (s) Pb2+ + 21- Ksp = [Pb2+1 [I-r *The greater the ksp the more soluble the solid is in 1-120. ](./media/image172.png)
Question 1 (b)
![(ii) Calculate the minimum concentration of F-(aq) necessary to
initiate precipitation of the salt selected in part (b)(i). 3.5 = =
3.5 x 10-10 = \[F-\]2 -10 = 10-5M 3.5 x 10 1 point is earned for the
correct value of \[F - \].](media/image173.png)
Question 3 (c)
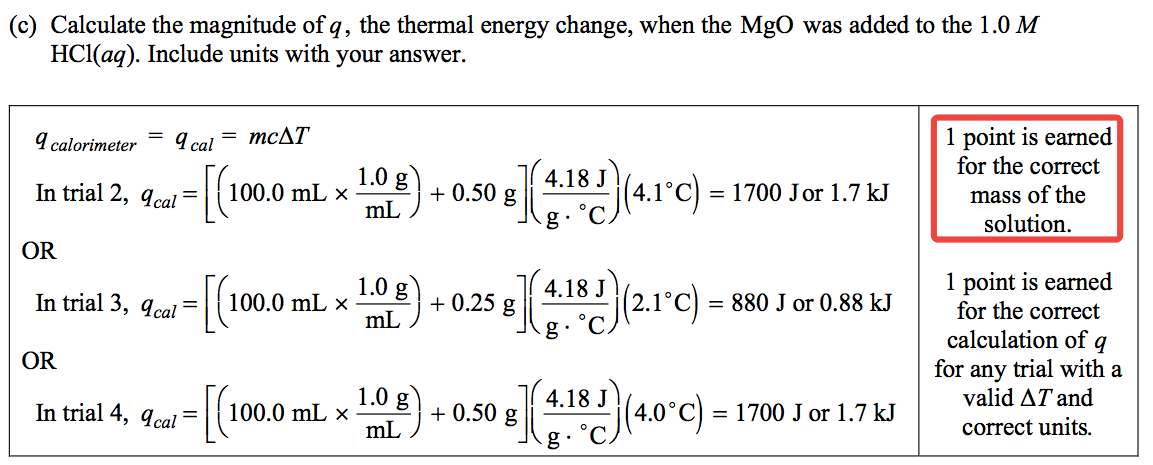
Question 3 (e)
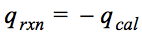
Question 4 (a)
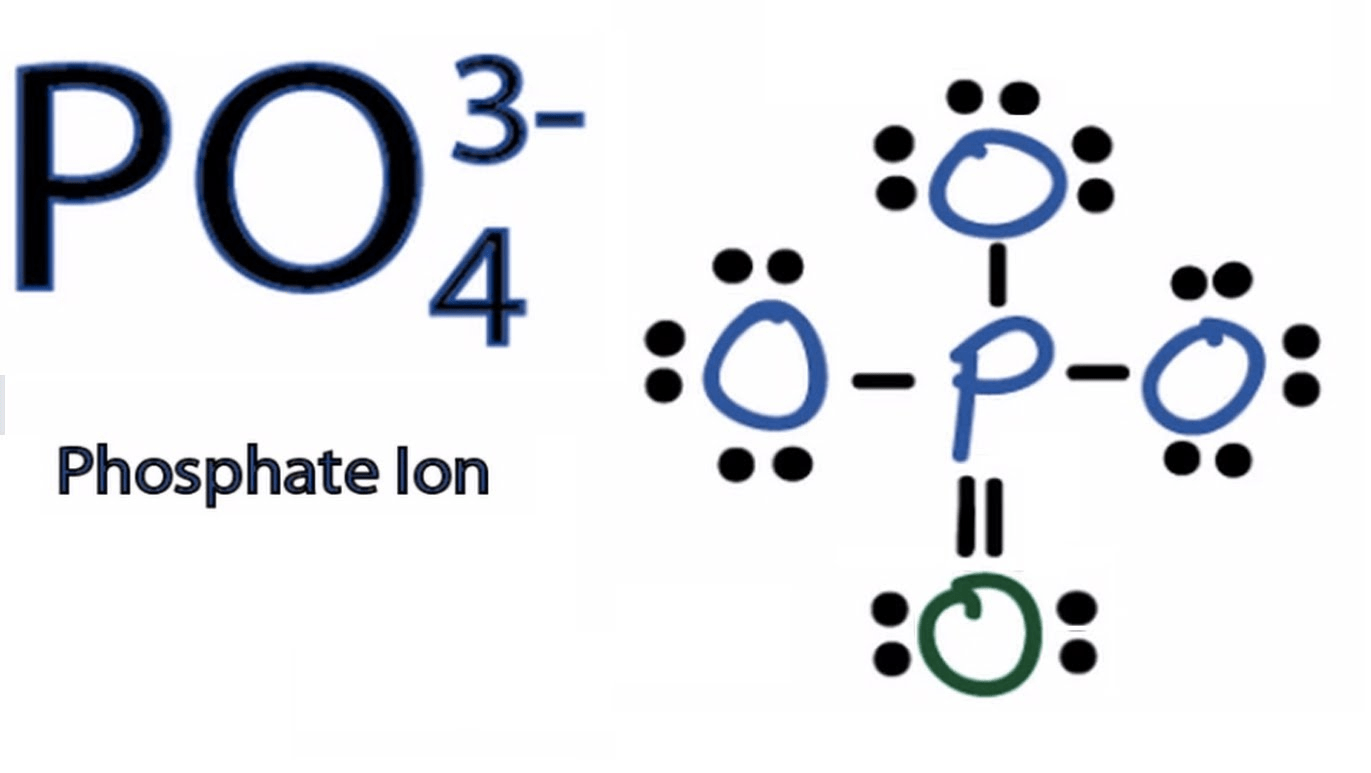
- Write ionic equation if possible
Question 5 (a)
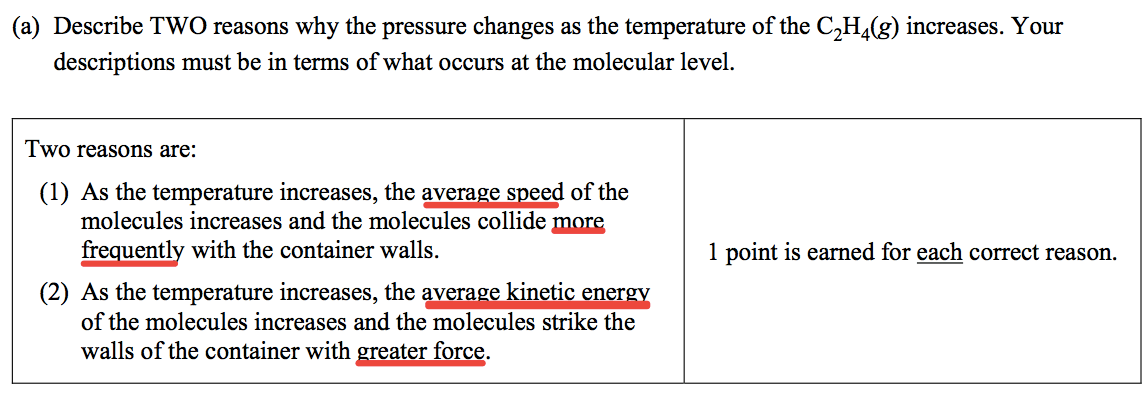
Question 5 (e)
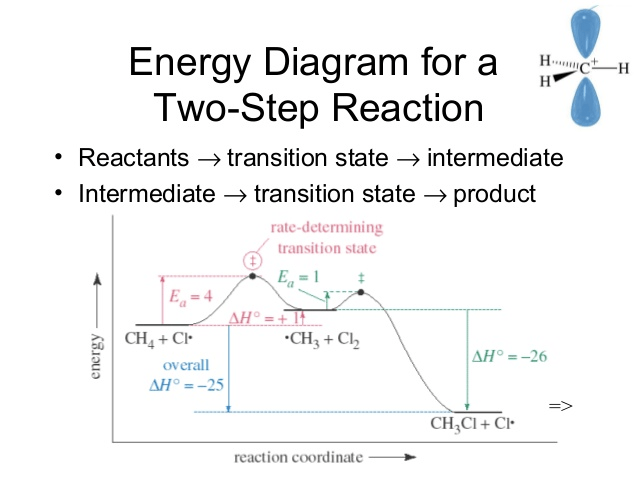
Question 6 (c)

Question 6 (e)
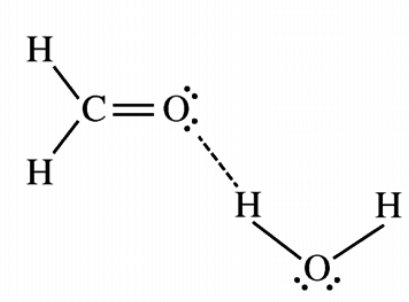
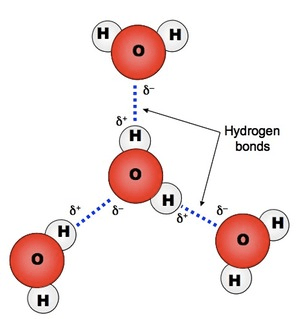
hydrogen bonding