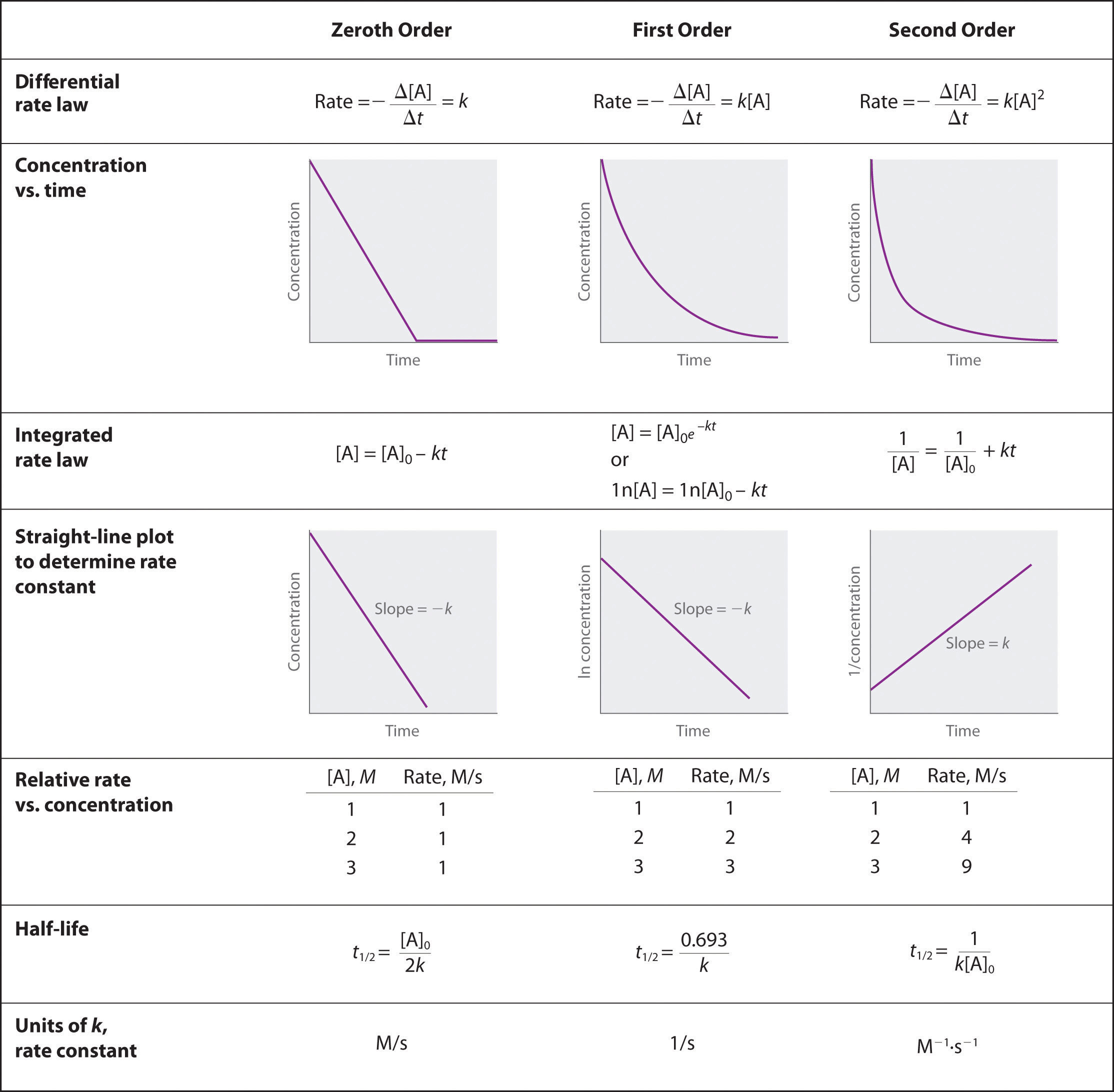
Question 4
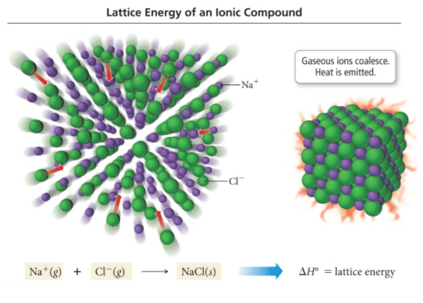
![计算机生成了可选文字: The principal reason ionic compounds are stable is the
attraction between ions Of opposite charge. This attraction draws the
ions together , releasing energy and causing the ions to form a solid
array , or lattice , such as that shown in Figure 8 . 3 . A measure of
how much stabilization results 什 om arranging oppositely charged ions
in an ionic solid is given by the lattice energy , which is the “ “ 罗
required co e 纱 separate 0 ” e mole Ofa solid io CO PO d 仂 its g eo io
. TO envision this process for NaCl, imagine that the structure in
Figure 8 . 3 expands from within , SO that the distances between the
ions increase until the ions are very far apart. This process requires
788 kJ/moI, which is the value of the lattice energy: NaC1(s) -- - 一 十
(g) + Cl-(g) AHIattice = +788kJ/moI \[ 8 . 3 \]](media/image6.png)
Question 9-12
Buffer
Weak Acid + Its Congregate Base
Weak Base + Its Congregate Acid
Question 13-16

Question 23
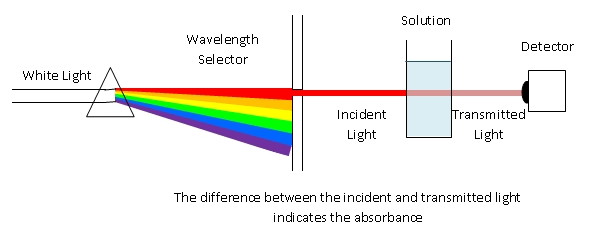
Question 27
A visible-light spectrophotometer can determine the concentration of a solution
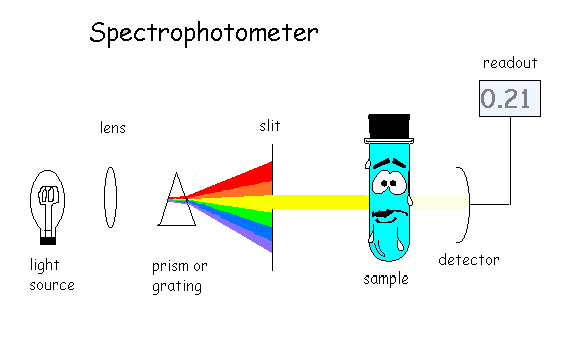
Question 30
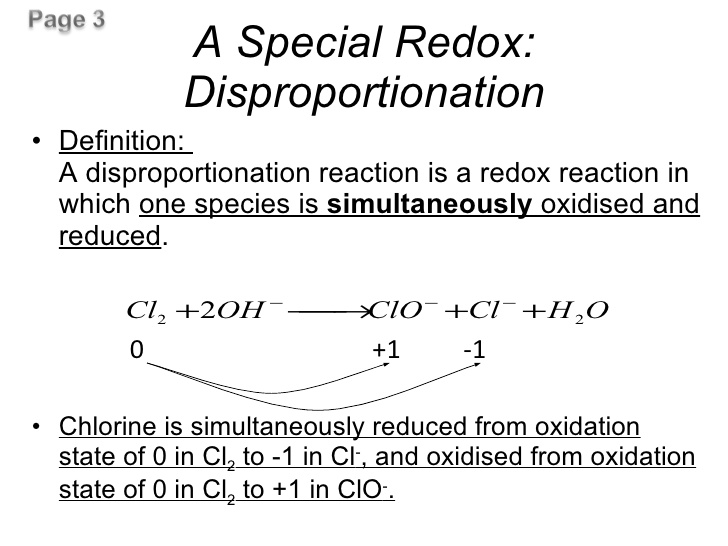
Question 31
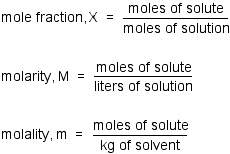
Question 32
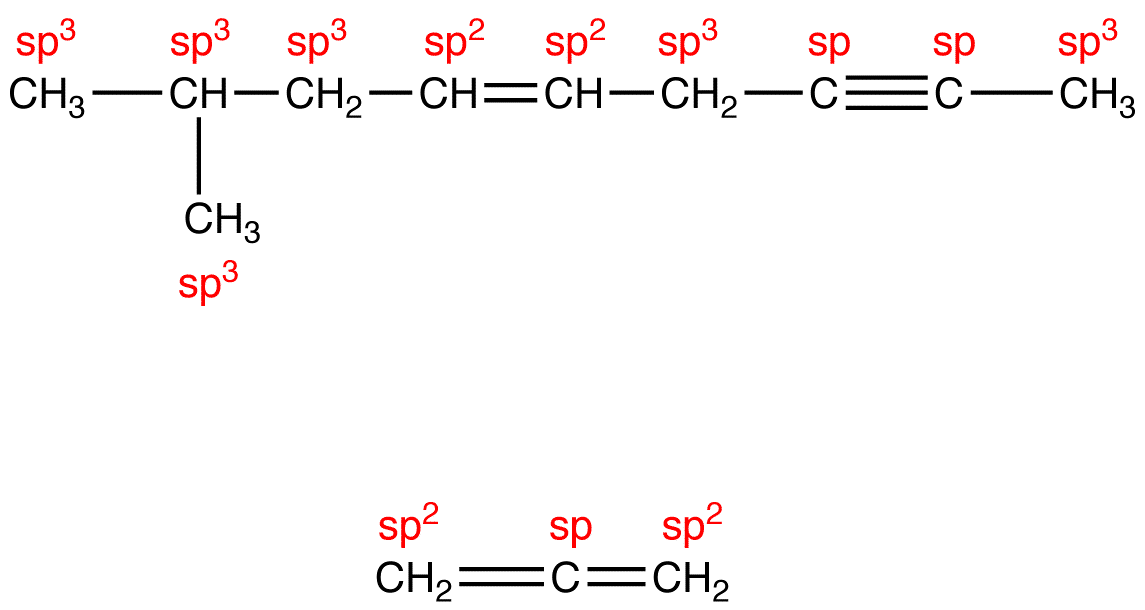
Question 35
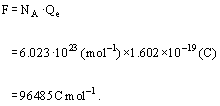
Question 38
Question 39
- The normal melting point of a solid is defined as the temperature at which the solid and liquid are in equilibrium at a total pressure of 1 atmosphere.
Question 43
When excess ammonia is added to a solution of Cu(NO3)2, the color of blue will be darker.
Cu(NO3)2 + 4NH3 = [Cu(NH3)4]](NO3)2

Adding Ammonia To Copper II Nitrate.
(left) Solution of blue Cu(NO3)2*6H2O (complex ion is Cu(H2O)6 +2).
(right) Addition of NH3(aq) forms deep blue complex ion [Cu(NH3)4(H2O)2]2+.
Question 53
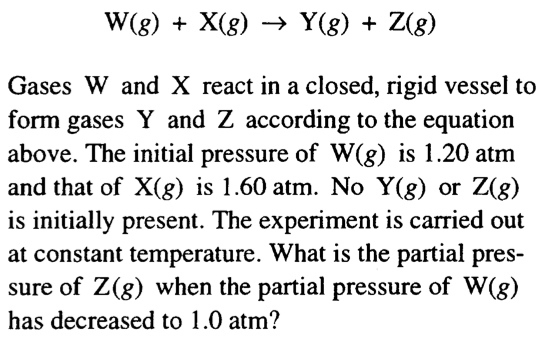
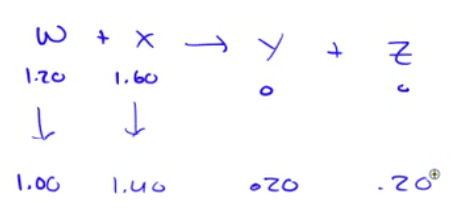
Question 54

Question 56

Question 57
- The standard reduction potential is an intrinsic property. It will not change by the coefficient.
Question 63
Question 54
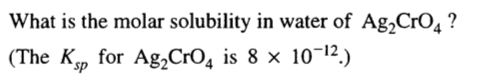
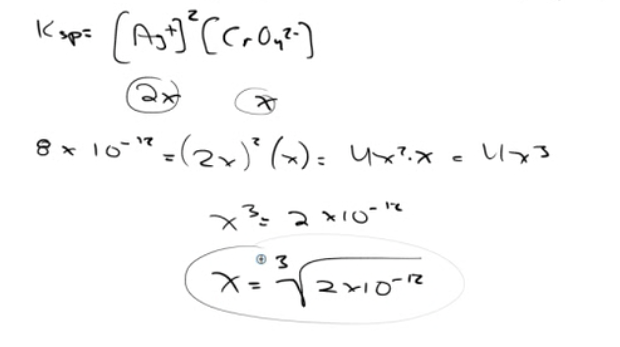
Question 70

Question 72

Question 74
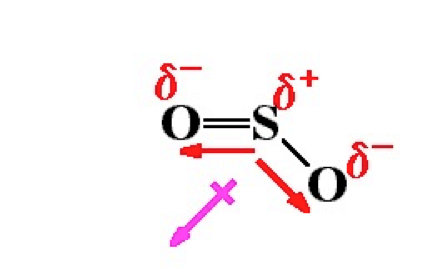
SO2 is a polar molecule, so it will deviate from ideal behavior.